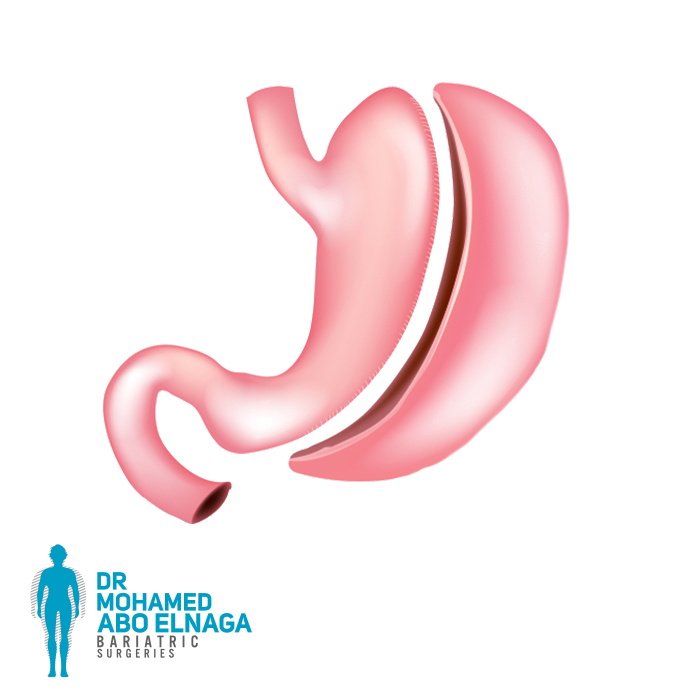
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy surgery
Many are talking about gallbladder pain and its difficulty. But not everyone knows what a gallbladder is, where it is located, why does it cause so much pain, and how to treat it?
In this article, we will discuss this topic.
We will start by defining the gallbladder:
It is a small organ in the human body that looks like a pear and contains the digestive bile juice secreted in the small intestine.
Where is the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is located below the liver, on the right side of the abdomen.
Is it normal for the gallbladder to be painful? And what could make the gallbladder cause so much pain?
It is not normal for the gallbladder to cause pain unless there is an inflammation or a pathological condition such as:
1- Obstruction of the bile duct:
There are twists and zigzags in the bile duct, which may cause its blockage, causing cholecystitis occurrence.
2- Infection:
Some diseases, such as HIV and other viral diseases, may cause inflammation of the gallbladder.
3- Tumor:
If there is a tumor obstructing the movement of bile from the gallbladder to the small intestine, bile accumulates in the gallbladder, resulting in inflammation.
4- Vascular disease:
Suffering from a disease that affects the function of blood vessels, which impedes adequate blood flow to the gallbladder, makes it vulnerable to inflammation.
5- Gallstones:
Gallstones are the most common cause of cholecystitis. Stone formation inside the gallbladder leads to blockage of the bile duct and thus cholecystitis.
What are the causes of gallstones formation?
There are many reasons, including:
1- Increasing the proportion of cholesterol secreted from the liver: The bile's function is to dissolve cholesterol, so if the liver secretes more cholesterol than the bile can dissolve, the undissolved cholesterol turns into stones.
2- The gallbladder cannot empty its juices well: In this case, bile accumulates in the gallbladder, causing the formation of stones.
3- A large amount of bilirubin in the bile juice: This often occurs due to some diseases, such as blood disorders, liver cirrhosis, and the case of cholecystitis.
4- Eating unhealthy foods: Rich-fat and poor-fiber meals increase the risk of developing gallstones.
5- Obesity: The accumulation of body fats and the ingestion of an unbalanced diet lead to gallstones.
6- Age: As a person becomes over 40 years old, the risk of developing gallstones increases.
7- Rapid and unhealthy weight loss: Increases the possibility of gallstones.
8- Pregnancy: Pregnant women are more likely to develop gallstones than others.
9- Contraceptives or estrogen-containing drugs.
10- Race: Mexican or North American people are more likely to suffer from gallstones.
11- Diabetic patients: Are susceptible to gallstones.
12- Genetic predisposition or family history: The family history of gallstones increases the chance of stone formation in the new generations.
13- Gender: Women are more prone to gallstones than men.
Types of gallstones:
Gallstones are divided into three types:
The first type: cholesterol gallstones:
They are yellow stones consisting of cholesterol that is not dissolved in the bile, and it accumulates to form these stones, and this type is the most common.
The second type: pigmented gallstones:
These stones are black or dark brown. They are formed due to an increase in the proportion of bilirubin in the bile.
The third type: mixed stones:
It is a mixture of cholesterol and calcium stones.
What are the symptoms of stones or gallbladder inflammation?
1- Severe and sudden pain occurs in the upper side of the abdomen.
2- The pain may be in the middle of the abdomen or below the thoracic cage.
3- Pain may also occur in the back, specifically between the shoulder blades, or in the right shoulder only.
4- A strong feeling of nausea that may reach vomiting.
5- A person may develop a fever.
6-Pain, when touching the abdomen, may last for several hours in some cases.
What is the treatment of cholecystitis and stones?
The best solution or treatment is laparoscopic cholecystectomy in cases of cholecystitis, bile duct obstruction, gallstones, or pancreatitis caused by gallstones.
How is laparoscopic cholecystectomy performed?
- It should be noted that laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a very simple surgery and does not take much time. The surgery takes an hour or two at most. Dr. Mohamed Abo El Naga makes four small surgical incisions to insert the laparoscope and other tools used to remove the gallbladder, and then sew these incisions after gall bladder removal.
- General anesthesia is required during the surgery.
- The patient can return home on the same day of the surgery or the next day as a maximum, or when the patient can eat and drink.
- The recovery period after laparoscopic cholecystectomy is not more than a week.
Before Cholecystectomy:
1- The patient must fast from 8 to 12 hours before performing the surgery.
2- The patient must inform the doctor of his full medical history to avoid complications during surgery.
3- Any medications or dietary supplements that may affect blood flow must stop before surgery.
After cholecystectomy:
1- The patient should move and walk after the surgery to avoid clots.
2- The patient must stop smoking for at least a week or until the wounds heal.
3- The patient must adhere to a healthy and balanced diet, rich in fiber and not containing harmful fats.
Are there complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic surgical intervention greatly reduces the incidence of complications of the traditional surgery because the surgical openings are much smaller, which provides the patient with the highest standards of safety and security during the surgery, less pain, a shorter recovery period, and no scars.
Some complications:
1- Bleeding.
2- Infection.
3- Bile leakage.
4- Injury of the organs adjacent to the gallbladder, such as the small intestine or the liver.
You can avoid all these complications by choosing a highly skilled and experienced surgeon like Dr. Mohamed Abo El Naga.
You must be well aware of the seriousness of delaying the surgical intervention to remove the gallbladder, as inflammation and gallstones can lead to:
1 - Rupture of the gallbladder, which exposes the patient to danger.
2- Gallbladder infection, due to the accumulation of bile inside the gallbladder.
3- The death of the gallbladder tissue or gangrene occurrence.

